
In the modern business landscape, reliance on technology by small business owners is increasing, fueling both growth and efficiency. Technology tools add many essential benefits but also introduce complex challenges with cybersecurity. A survey conducted by Connectwise in 2022 revealed a startling trend: 76% of small businesses had fallen victim to at least one cyberattack, a significant surge from 2020 when only 55% reported such an experience. The data underscores the critical importance for small business owners to safeguard digital assets.
Cybersecurity is a vast and complex field, with numerous aspects for businesses to consider. The task of shoring up security may seem overwhelming and daunting. To simplify this challenge, here are five actionable steps to enhance small business cybersecurity.
1. Inventory Technology Assets
Begin with identifying vulnerabilities potential threats can exploit to access business data. Understanding the technology, you have in your small business is the foundation of a robust cybersecurity strategy.
- Why it’s vital: Knowing what devices are connected to your network helps you monitor and control access. Neglecting this can lead to unauthorized access, resulting in data loss or manipulation of sensitive information.
- How to do it: Create a detailed inventory list of all devices, including their make, model, and purpose. Regularly update this list to reflect any changes.
2. Ensure Technology is Up to Date
Once you know what technology you have within your business, keep it current. Keeping technology up to date is a critical cybersecurity measure for small businesses.
- Why it’s vital: Hackers often exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated systems. Keeping technology up to date ensures that you have the latest security patches. Failure to update can lead to financial loss due to cyberattacks.
- How to do it: Regularly check for updates for your operating system, antivirus software, and other critical applications. Enable automatic updates where possible.
- Checking for Updates: Most operating systems and software have an option to check for updates in the settings or preferences menu. For hardware, consult the manufacturer’s website or support for firmware updates.
3. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication and Unique Passwords in Your Small Business
Passwords and logins are often the first line of defense in small business cybersecurity.
- Why it’s vital: Simple or reused passwords can be easily cracked. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security. Ignoring this can lead to reputational damage if personal or financial information is compromised.
- How to do it: Encourage employees to use strong, unique passwords for different accounts. Implement multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
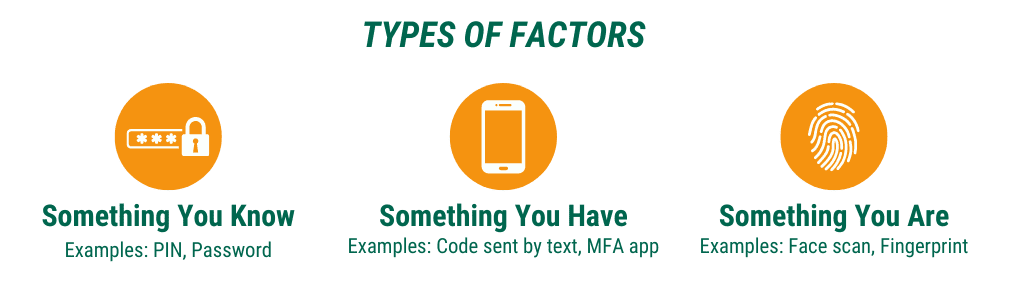
- Understanding Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Multi-factor Authentication, also known as MFA or Two-Step Verification, is a security process that requires more than just a username and password to verify the user’s identity. Traditional authentication methods that rely solely on usernames and passwords are often inadequate, as usernames can be easily discovered, and passwords may be simple or reused across different sites. MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring a second “factor” to prove who you are. This second factor can be something you know (like a password or PIN), something you have (like a smartphone or secure USB key), or something you are (like a fingerprint or facial recognition).
4. Install a Firewall for Your Small Business
A firewall is a fundamental cybersecurity measure for small businesses. Implementing a firewall can prevent DDoS attacks, which saw a 60% increase in malicious attacks in the first half of 2022.
- Why it’s vital: Firewalls filter incoming and outgoing traffic. Without a firewall, networks are exposed to potential threats.
- How to do it: Consider both software and hardware firewalls. Ensure that remote employees also have adequate protection.
- Understanding Firewalls: A firewall is a crucial component of cybersecurity, especially for small businesses. It serves as a virtual barrier between your internal network and the external internet, monitoring and controlling the flow of traffic based on predetermined security rules. There are two main types of firewalls: hardware firewalls and software firewalls. A hardware firewall is a physical device that sits between a network and the internet, while a software firewall is installed on individual computers within a network.
5. Educate Staff on Cybersecurity in Your Small Business
Your employees play a crucial role in any small business cybersecurity strategy. In fact, according to Gartner, “82% of data breaches were a result of employee behaviors that were unsecure or inadvertent.”
- Why it’s vital: Human error can lead to breaches. Educating staff about common cyber threats and safe practices can prevent many potential attacks.
- How to do it: Conduct regular training sessions and education, including:
- Workshops and Seminars: Regularly conduct workshops to educate employees about the latest threats and safe online practices.
- Online Resources: Share informative articles, videos, and tutorials.
- Simulated Attacks: Conduct simulated phishing attacks to test employees’ awareness and provide feedback.
- Regular Reminders: Send regular email reminders about safe practices, updates, and company policies.
Cybersecurity is not just a concern for large corporations; it’s a vital consideration for every size business. By taking these five actionable steps, you can significantly enhance the cybersecurity posture of your small business. For a more comprehensive list of things you can do to protect your business, download our Cybersecurity Essentials Checklist for Small and Medium Sized Businesses.
At Back To Business I.T., we offer comprehensive cybersecurity services tailored to your needs. If you are looking for assistance with your cybersecurity strategy, contact us today.